Improving Essential Tremor
More than 13 Million people in the US currently suffer from hand tremors. This silent disease causes involuntary muscle contractions that can make daily activities like eating, drinking, writing, and brushing teeth nearly impossible. While there are several assistive devices currently on the market, they either address only specific activities (like writing or eating) or they are very expensive.
Our objective was to design a low-cost assistive device for people with hand tremors to perform activities of daily living with more independence. The device must be:
Easy to hold; Easy to deploy and store/take with
Accessible to the general public
Able to accommodate many different tasks
Market Gap in Hand Tremor Treatments: Optimal Cost and Efficacy
Technological Gap: Combining Active (top) and Passive (bottom) Impedance
Solution: Combining passive and active impedance
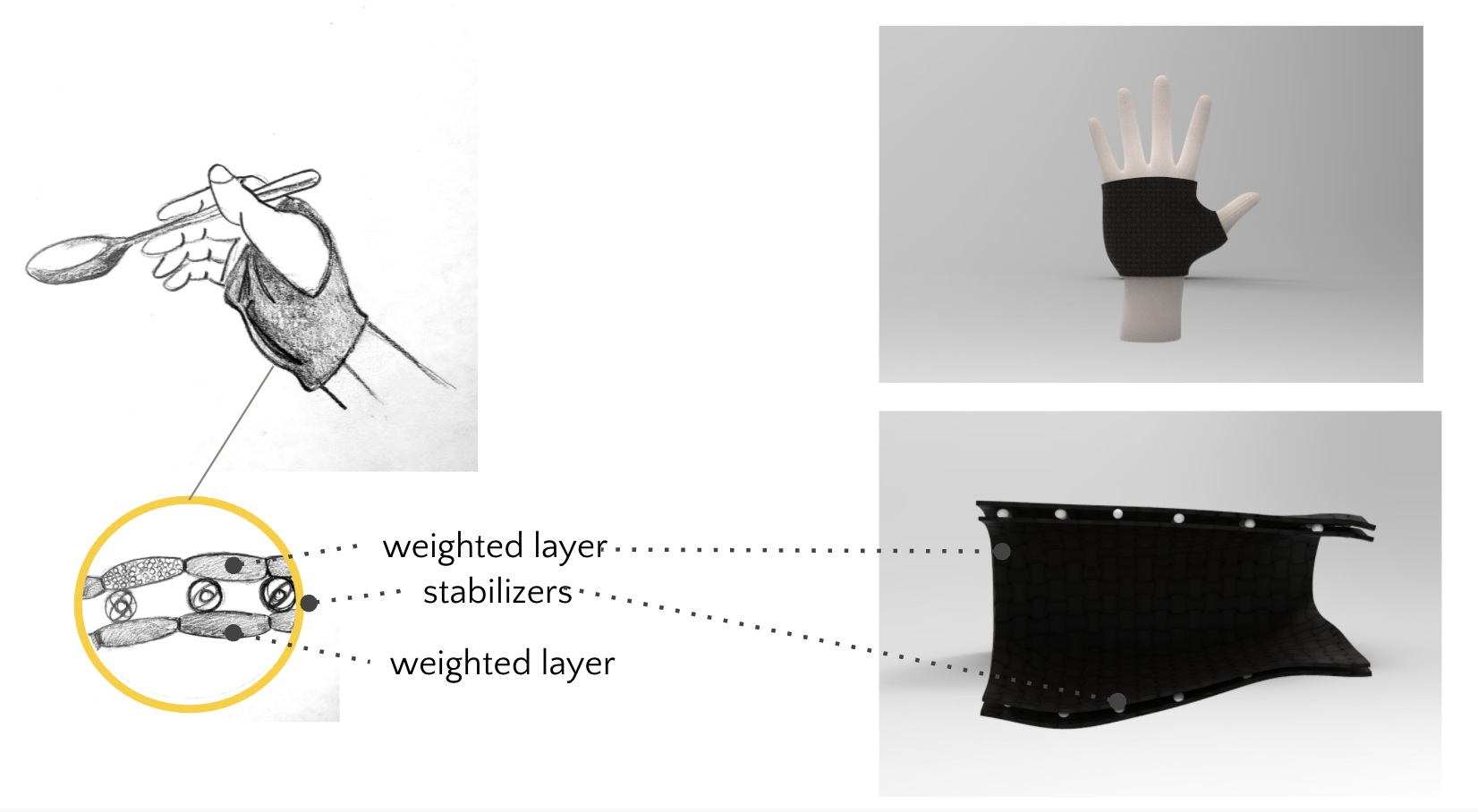
The passive impedance mechanism involves the weighted material of the glove being able to oppose the motion of the tremor automatically (as a result of the tremor acting up). In doing so, the glove will be able to shift its center of balance to counter it without having to apply any additional force. The active impedance mechanism uses gyroscopes or stabilizers implanted throughout the glove to help identify the tremor vectors and velocities, calculate a way to counteract this spontaneous movement, and implement said countermeasures.
Structure of the glove includes weight for passive impedance and gyroscopic sensors for active impedance.
Active impedance, followed by the passive unit which will detect the orientation of the hand and continuously sense the tremerous motion in the hand. It will then be programmed to filter out the frequency range of 6-12 hertz which is the tremor frequency. These signals will be amplified and filtered and averaged out before a reverse signal is sent back to the hand through an actuator.
Prototype: Glove with a top neoprene layer filled with weight gravel to achieve passive impedance.
Testing
The Archimedes spiral test: The spirals drawn by someone with essential tremor usually presents as spirals with higher frequency, smaller amplitude, and more symmetry.
Objective data monitoring to record the frequency and amplitude of tremor, then determine whether or not the patient’s tremor fits into one of the major tremor syndromes.
Archimedes spiral test
Objective Data Monitoring: Tremor: >2 Hz , Voluntary motion: < 2 Hz
You can view the full report here.